Dumbarton Combination, Dunbartonshire
The Dumbarton Combination, formed in 1861, comprised the 13 parishes of Bonhill, Buchannan, Cardross, Drymen, Dumbarton, Kilmaronock, New Kilpatrick, Old Kilpatrick, Kippen, Luss, Port of Monteith, Roseneath and Row. The total population of the member parishes in 1881 was 67,409.
The Dumbarton Combination poorhouse, designed by James Campbell Walker, was erected in 1862-5 on Townend Road at the northern outskirts of Dumbarton. It could accommodate 134 inmates. An additional infirmary block was added in 1866, probably to house lunatic inmates who numbered up to 60.
The poorhouse site location and layout are shown on the 1930s map below.
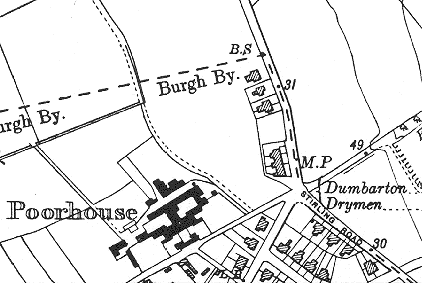
Dumbarton site, 1938.

Dumbarton former poorhouse site from the south, early 1980s.
© Martin Wardrop

Dumbarton former poorhouse site from the south, early 1980s.
© Martin Wardrop
In 1902, an official inspection of the poorhouse lunatic wards noted some recent improvements:
In 1913, the poorhouse was partially destroyed by a fire which began in a defective chimney in the main block. The fire occured during the day and none of the inmates was harmed, although a few had to be temporarily be boarded at other poorhouses.
The poorhouse later became Townend Poor Law Institution. In 1946 it had 186 beds and a hospital with 78 beds. After 1948, it became Townend Hospital, and then the Central Hospital, providing geriatric care until its closure in the early 1980s.
The buildings have been demolished and the Langcraigs old people's home now stands on the site.
Staff
Inmates
Records
Note: many repositories impose a closure period of up to 100 years for records identifying individuals. Before travelling a long distance, always check that the records you want to consult will be available.
- West Dunbartonshire Archives, Strathleven Place, Dumbarton G82 1BD, Scotland. Dumbarton Combination Poorhouse minutes (1861-1954).
Bibliography
- None.
Links
- None.
Acknowledgments
- Thanks to Martin Wardrop for providing the pictures.
Unless otherwise indicated, this page () is copyright Peter Higginbotham. Contents may not be reproduced without permission.


