Whitby, North Riding of Yorkshire
Up to 1834
The first Whitby workhouse, funded by public subscription, was built in 1726-7 on Church Street. A parliamentary report of 1777 recorded a local workhouse in operation in the town for up to 70 inmates. In 1793-4, a new workhouse was erected off Green Lane at the south-east of the town. Being located near the entrance to Boulby's ropery, the site became known as The Ropery. The new building was L-shaped in layout as shown on a map of 1828.
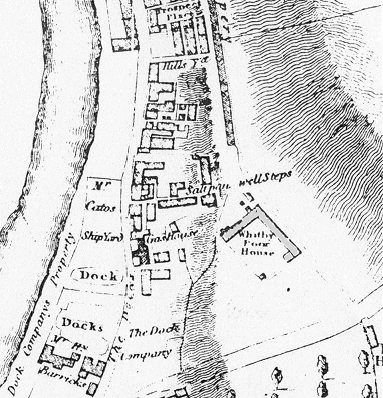
Whitby workhouse site, 1828
The Ruswarp township workhouse, 'a handsome stone house', was built by subscription in 1804. It stood at the west side of Whitby, at the rear of what is now 82 Stakesby Road. It seldom had above 40 inmates. The building no longer exists.
After 1834
Whitby Poor Law Union formally came into existence on 9th January 1837. Its operation was overseen by an elected Board of Guardians, 24 in number, representing its 22 constituent parishes and townships as listed below (figures in brackets indicate numbers of Guardians if more than one):
North Riding of Yorkshire:
Aislaby, Barnby, Barrowby, Egton, Ellerby, Fylingdales, Glaisdale, Goadland or Goatland, Hawkser with Stainsiker, Hinderwell, Lythe, Mickleby, Hutton Mulgrave, Newton Mulgrave, Newholm with Dunsley, Roxby, Ruswarp, Sneaton, Ugglebarnby, Ugthorpe, Whitby (3).
Later Additions:
Eskdaleside (from 1837), Helredale (from 1894).
The population falling within the Union at the 1831 census had been 19,882 with parishes and townships ranging in size from Ellerby (population 64) to Whitby itself (7,765). The average annual poor-rate expenditure for the period 1834-36 had been £5,532 or 5s.7d. per head of the population.
The new Whitby Union took over the existing workhouse in 1837. It layout in 1849 is shown below.
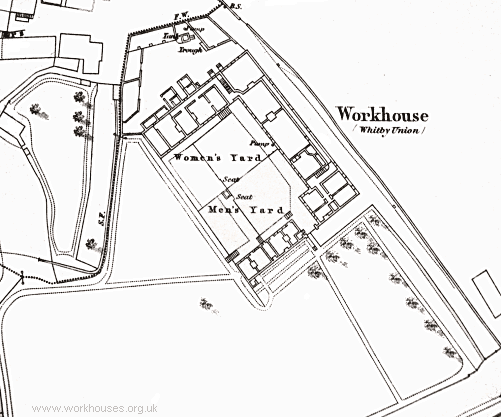
Whitby workhouse site, 1849
In 1860, it was enlarged to about twice its size, forming a large U-shape. An entrance block was added at the south, and a school was also erected at the rear of the workhouse. The architects for the expansion scheme were John and William Atkinson of York who were responsible for a number of other Yorkshire workhouses including Bedale, Beverley, Easingwold, Goole, Howden, Pocklington, Skirlaugh and York. The workhouse location and layout are shown on the 1911 OS map below.
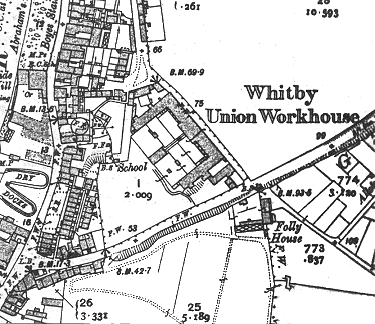
Whitby workhouse site, 1911

Whitby main block from the south-east, 2001.
© Peter Higginbotham.

Whitby main block from the south-east, 2001.
© Peter Higginbotham.

Whitby rear of main block from the south-west, 2001.
© Peter Higginbotham.

Whitby entrance block from the south-east, 2001.
© Peter Higginbotham.
In 1930, Boards of Guardians were abolished and local councils took over the administration of poor relief. Under the control of the North Riding County Council, the workhouse was redesignated as a Public Assistance Institution.

Whitby's final Board of Guardians on a visit to Mulgrave Castle, 1930.
© Peter Higginbotham.
After the inauguration of the National Health Service in 1948, the former workhouse became St Hilda's Hospital and provided geriatric care. St Hilda's closed in 1978 and the surviving buildings are now occupied by small business units.
Staff
Inmates
Records
Note: many repositories impose a closure period of up to 100 years for records identifying individuals. Before travelling a long distance, always check that the records you want to consult will be available.
- North Yorkshire County Record Office, Malpas Road, Northallerton DL7 8TB. Very limited holdings include Guardians' minutes (1837-81).
Bibliography
Links
- None.
Unless otherwise indicated, this page () is copyright Peter Higginbotham. Contents may not be reproduced without permission.


