Kington, Herefordshire
Up to 1834
Kington had a workhouse by 1734. In 1776, it could house up to 40 inmates. At the same date, a workhousee at Pembridge accommodated up to 30 paupers.
After 1834
Kington Poor Law Union was officially formed on 25th August 1836. Its operation was overseen by an elected Board of Guardians, 29 in number, representing its 26 constituent parishes as listed below (figures in brackets indicate numbers of Guardians if more than one):
County of Hereford:
Kington (3); Brilley; Eardisley; Lower Harton; Huntington; Lyonshall or Lynhales; Pembridge (2); Staunton-on-Arrow; Titley; Willersley; Winforton.
County of Radnor:
Colva; Ednol; Evenjobb, Newcastle, Barland and Burva; Gladestry; Glascwm; Harpton; Kinnerton, Salford and Badland; Llandegley; Llanfihangel Nant Melan; Michaelchurch-on-Arrow; Newchurch; New Radnor; Old Radnor and Burlinjobb; Trewern and Gwithla; Walton and Womaston.
Later Additions: Byton; Combe; Lower Kinsham; Upper Kinsham; Knill; Lingen; Rodd, Nash and Little Brampton; Stapleton; Willey (all from 1836); Byton, Combe, Kinsham, Knill, Lingen; Rod, Nash and Little Brampton; Stapleton, Willey (all from 1877).
The population falling within the union at the 1831 census had been 12,022 with parished rangingin size from Willersley (population 13) to Kington itself (3,111). The average annual poor-rate expenditure for the period 1833-35 had been £6,425 or 10s.8d. per head of the population.
The new Kington Union board of Guardians met for the first time on 26th August 1836. A Building Committee was formed to find a site and obtain for a workhouse. On the 30th August, the Clerk was instructed to advertise for plans, specifications and tenders for a workhouse for 150-250 persons. It was eventually decided to adopt the plans submitted by HJ Whitling which were for a building for 180 inmates and costing £2,800. Whitling was also the architect of the workhouses at Clun, Bridport, and East Retford. In order to reduce costs the design was amended and the revised version approved by the Poor Law Commissioners on 16th December 1836. The workhouse was built in 1837 at a site on the east side of Kingswood Road to the south of Kington. The workhouse location and layout are shown on the 1902 map below.
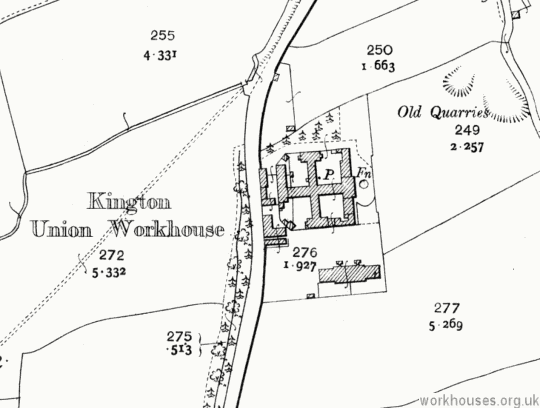
Kington workhouse site, 1902.
The workhouse followed the popular cruciform or "square" plan with an entrance block at the east, behind which lay the four accommodation wings radiating from a central hub, creating yards for the different classes of pauper (male/female, old/young). A detached infirmary was erected to the south in 1901.
In 1877, the union was enlarged by the addition of seven parishes and townships that previously formed part of the dissolved Presteigne Union.
In 1900-1, a detached infirmary was erected at the south of the workhouse. During the early part of the First World War it was used as a Red Cross Hospital.
In 1930, the site was taken over as by Herefordshire Council and became a Public Assistance Institution. The former workhouse was rebuilt as Kingswood Hall nursing home in about 1962.

Kington former workhouse site from the north-west, 2001.
© Peter Higginbotham.
Staff
Inmates
Records
Note: many repositories impose a closure period of up to 100 years for records identifying individuals. Before travelling a long distance, always check that the records you want to consult will be available.
- Herefordshire Archives and Record Centre, Fir Tree Lane, Hereford HR2 6LA. Holdings include: Guardians' minute books (1836-1930 with gaps); Admissions and discharges (1906-27); Creed registers (1905-12).
Bibliography
- Higginbotham, Peter The Workhouse Encyclopedia (2014, The History Press)
Links
- None.
Unless otherwise indicated, this page () is copyright Peter Higginbotham. Contents may not be reproduced without permission.


